AES 대칭키 알고리즘 with Golang
Prologue
대개 금융사와 연동할 때는 통신시에 암호화를 한다. 암호에는 여러 방법이 있지만 필드에서 가장 보편적으로 쓰이고 있는 AES 대칭키 알고리즘에 대해 이야기 하고, Golang으로 구현한 내용을 공유한다.
AES(Advanced Encryption Standard) 알고리즘이란?
말 그대로, 고급 암호화 표준이다. 2001년에 미국 표준 기술 연구소에서 AES 공모전을 열었고 Rijndael(레인달) 알고리즘이 채택 되었다. AES는 암호화와 복호화 과정에서 동일한 키를 사용하는 대칭 키 알고리즘이다.
암호키의 길이는 AES-128, AES-192, AES-256이 있는데 각각 16, 24, 32글자(byte)로 작성할 수 있다.
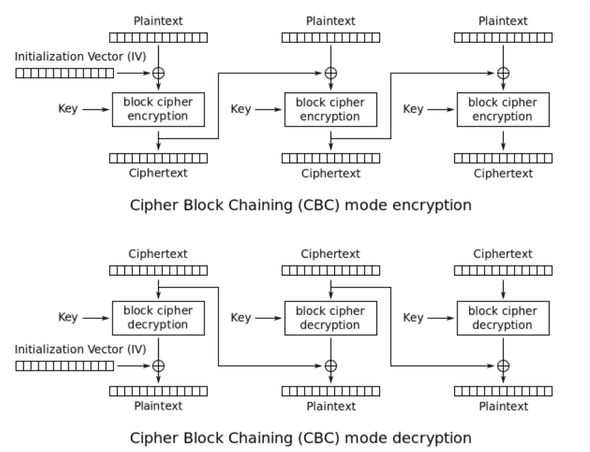
CBC(Cipher Block Chaining) Mode
실무에서는 데이터의 크기가 크기 때문에 16byte씩 잘라서 암호화 한다. CBC는 블록 암호화 운영 모드 중 보안성이 제일 높은 암호화 방법이고 가장 많이 사용된다.
평문의 각 블록은 XOR연산을 통해 이전 암호문과 연산되고 첫번째 암호문에 대해서는 IV(Initial Vector)가 암호문 대신 사용된다. 이 때 IV는 제 2의 키가 될 수 있다.
암호문이 블록의 배수가 되기 때문에 복호화 후 평문을 얻기 위해서 Padding을 해야만 한다.
암호화가 병렬처리가 아닌 순차적으로 수행되어야 한다.
Golang으로 AES-256 CBC모드 구현하기
go에서는 관련된 함수들을 crypto 패키지에서 제공한다.
func NewCipher(key []byte) (cipher.Block, error) : 대칭키 암호화 블록 생성
func NewCipher(key []byte) (cipher.Block, error) {
k := len(key)
switch k {
default:
return nil, KeySizeError(k)
case 16, 24, 32:
break
}
return newCipher(key)
}func NewCBCEncrypter(b Block, iv []byte) BlockMode : 암호화 블록과 IV로 암호화 블록 모드 인스턴스 생성
func (x *cbcEncrypter) CryptBlocks(dst, src []byte) : 암호화 블록 모드 인스턴스로 암호화
func NewCBCDecrypter(b Block, iv []byte) BlockMode : 암호화 블록과 IV로 복호화 블록 모드 인스턴스 생성
func (x *cbcDecrypter) CryptBlocks(dst, src []byte) : 복호화 블록 모드 인스턴스로 복호화
블록 암호화는 암호화할 데이터의 길이가 블록크기(aes.BlockSize == 16)의 배수 이어야 한다. 블록 크기에서 모자라는 padding으로 채워 줘야 한다.
encryptor, decryptor 구현
package cipher
import (
"bytes"
"crypto/aes"
"crypto/cipher"
"encoding/base64"
"strings"
)
type Crypto interface {
Encrypt(plainText string) (string, error)
Decrypt(cipherIvKey string) (string, error)
}
type niceCrypto struct {
cipherKey string
cipherIvKey string
}
func (c niceCrypto) Encrypt(plainText string) (string, error) {
if strings.TrimSpace(plainText) == "" {
return plainText, nil
}
block, err := aes.NewCipher([]byte(c.cipherKey))
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
encrypter := cipher.NewCBCEncrypter(block, []byte(c.cipherIvKey))
paddedPlainText := padPKCS7([]byte(plainText), encrypter.BlockSize())
cipherText := make([]byte, len(paddedPlainText))
// CryptBlocks 함수에 데이터(paddedPlainText)와 암호화 될 데이터를 저장할 슬라이스(cipherText)를 넣으면 암호화가 된다.
encrypter.CryptBlocks(cipherText, paddedPlainText)
return base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(cipherText), nil
}
func (c niceCrypto) Decrypt(cipherText string) (string, error) {
if strings.TrimSpace(cipherText) == "" {
return cipherText, nil
}
decodedCipherText, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(cipherText)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
block, err := aes.NewCipher([]byte(c.cipherKey))
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
decrypter := cipher.NewCBCDecrypter(block, []byte(c.cipherIvKey))
plainText := make([]byte, len(decodedCipherText))
decrypter.CryptBlocks(plainText, decodedCipherText)
trimmedPlainText := trimPKCS5(plainText)
return string(trimmedPlainText), nil
}
func NewNiceCrypto(cipherKey, cipherIvKey) (Crypto, error) {
if ck := len(cipherKey); ck != 32 {
return nil, aes.KeySizeError(ck)
}
if cik := len(cipherIvKey); cik != 16 {
return nil, aes.KeySizeError(cik)
}
return &niceCrypto{cipherKey, cipherIvKey}
}
func padPKCS7(plainText []byte, blockSize int) []byte {
padding := blockSize - len(plainText)%blockSize
padText := bytes.Repeat([]byte{byte(padding)}, padding)
return append(plainText, padText...)
}
func trimPKCS5(text []byte) []byte {
padding := text[len(text)-1]
return text[:len(text)-int(padding)]
}테스트 코드
package cipher
import (
"testing"
"github.com/stretchr/testify/assert"
)
func TestEncrypt(t *testing.T) {
t.Run("valid key size", func(t *testing.T) {
cipherKey := "CIPHERKEY01234567890123456789012"
cipherIvKey := "CIPHERIVKEY01234"
c, err := NewNiceCrypto(cipherKey, cipherIvKey)
assert.NoError(t, err)
assert.Equal(t, &niceCrypto{cipherKey, cipherIvKey}, c)
})
t.Run("invalid key size", func(t *testing.T) {
cipherKey := "CIPHERKEY01234567"
cipherIvKey := "CIPHERIVKEY"
_, err := NewNiceCrypto(cipherKey, cipherIvKey)
assert.Error(err)
})
t.Run("plain test `Abel Ko` should be equal `HD4PbbIOrV10Qc/+/7e+IA==`", func(t *testing.T) {
cipherKey := "CIPHERKEY01234567890123456789012"
cipherIvKey := "CIPHERIVKEY01234"
plainText := "Abel Ko"
expected := "HD4PbbIOrV10Qc/+/7e+IA=="
c, err := NewNiceCrypto(cipherKey, cipherIvKey)
assert.NoError(t, err)
cipher, err := c.Encrypt(plainText)
assert.NoError(t, err)
assert.EqualValues(t, expected, cipher)
})
}
func TestDecrypt(t *testing.T) {
t.Run("decrypted text `bgyE7m4EeLqQvtKnihJMfg==` should be equal `Abel Ko`", func(t *testing.T) {
cipherKey := "CIPHERKEY01234567890123456789012"
cipherIvKey := "CIPHERIVKEY01234"
chiperText := "HD4PbbIOrV10Qc/+/7e+IA=="
expected := "Abel Ko"
c, err := NewNiceCrypto(cipherKey, cipherIvKey)
assert.NoError(t, err)
actual, err := c.Decrypt(chiperText)
assert.NoError(t, err)
assert.EqualValues(t, expected, actual)
})
}